Our lives are a blip in the space time continuum. As a result, it can seem that the Earth is relatively static, with many of the large scale dynamic changes that shape our sphere largely unnoticeable to us occurring on geological time-scales. One such change is the movement of landmasses on earth, better known as plate tectonics.
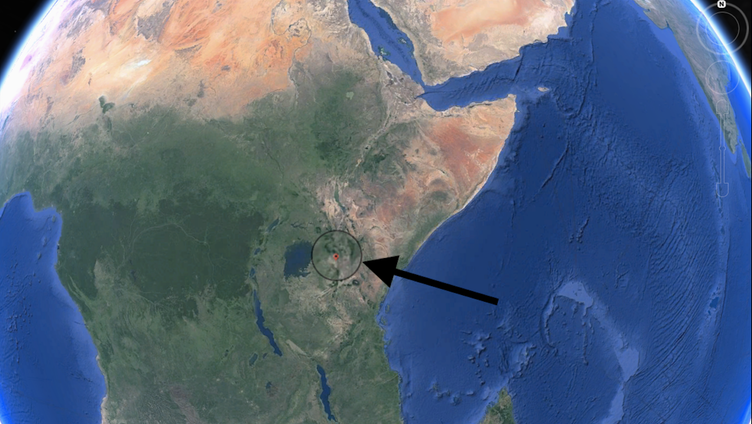
Earth’s landmasses are not static but in constant flux. The Earth’s lithosphere (formed by the crust and the upper part of the mantle) is broken up into a number of tectonic plates that move relative to each other at varying speeds, “gliding” over a viscous asthenosphere. There is still ongoing debate about what force or forces causes this movement, but whatever the forces are they can also cause the plates to rupture, forming rifts, and potential leading to the development of new plate boundaries. When this happens landmasses break-up and new continents forms; this is currently happening in the East African Rift in southwestern Kenya.