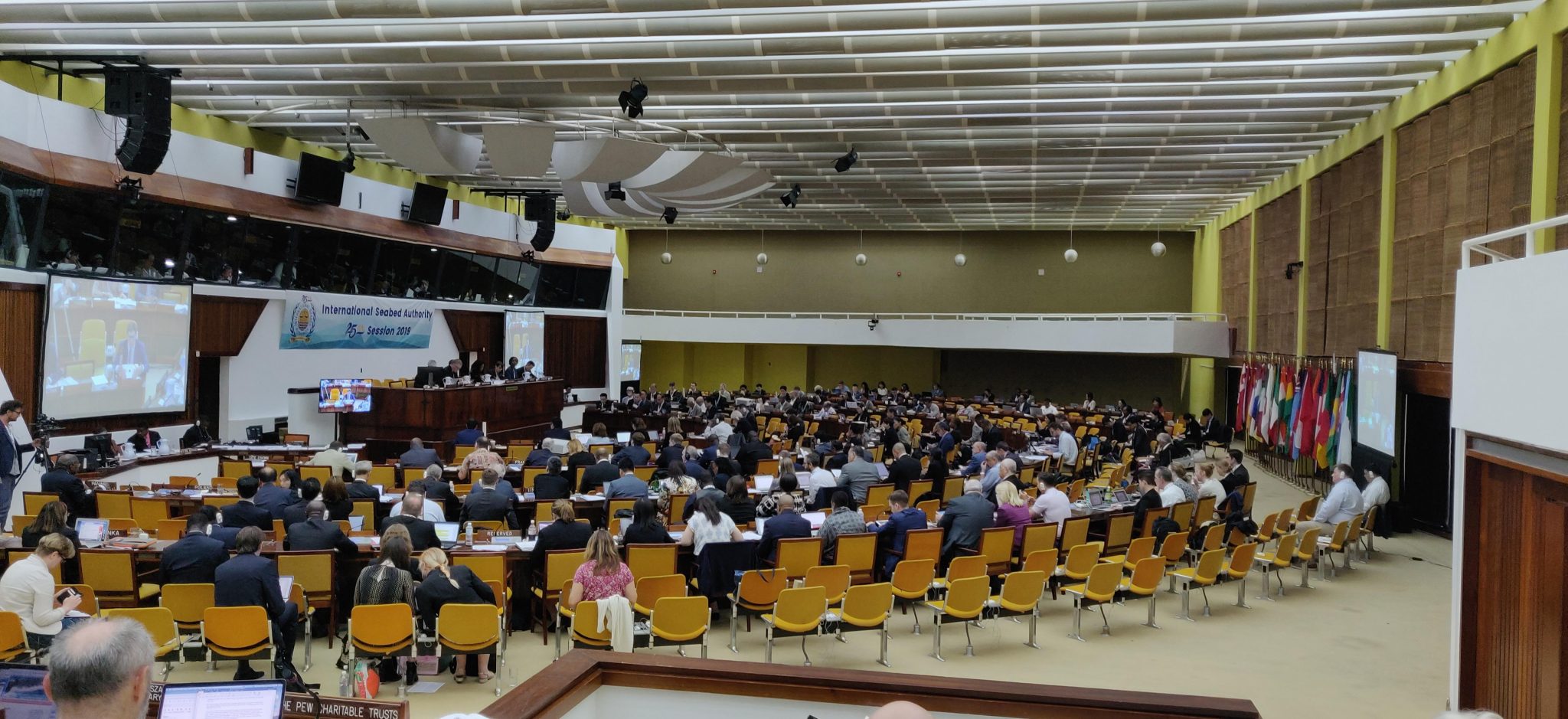
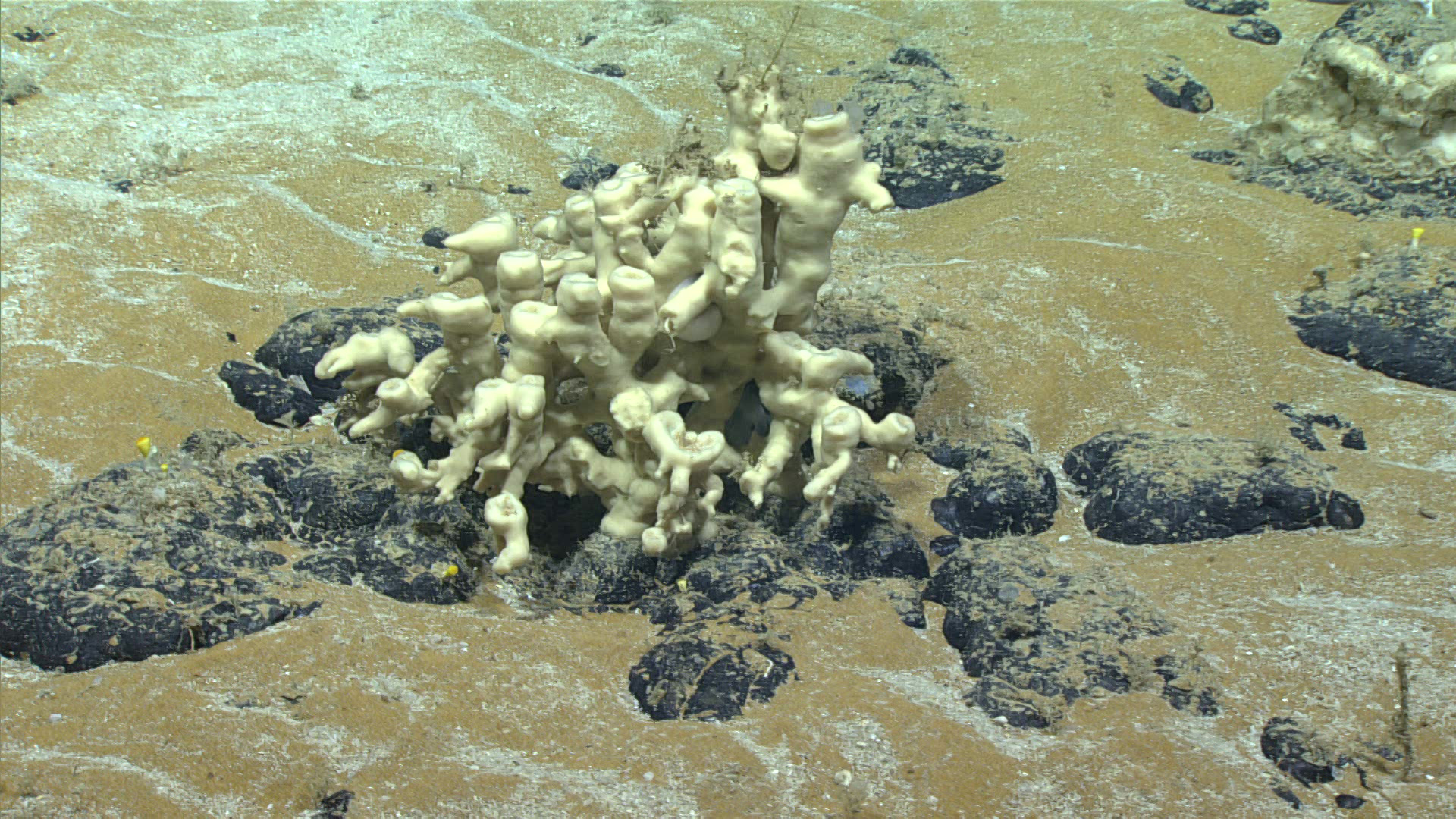
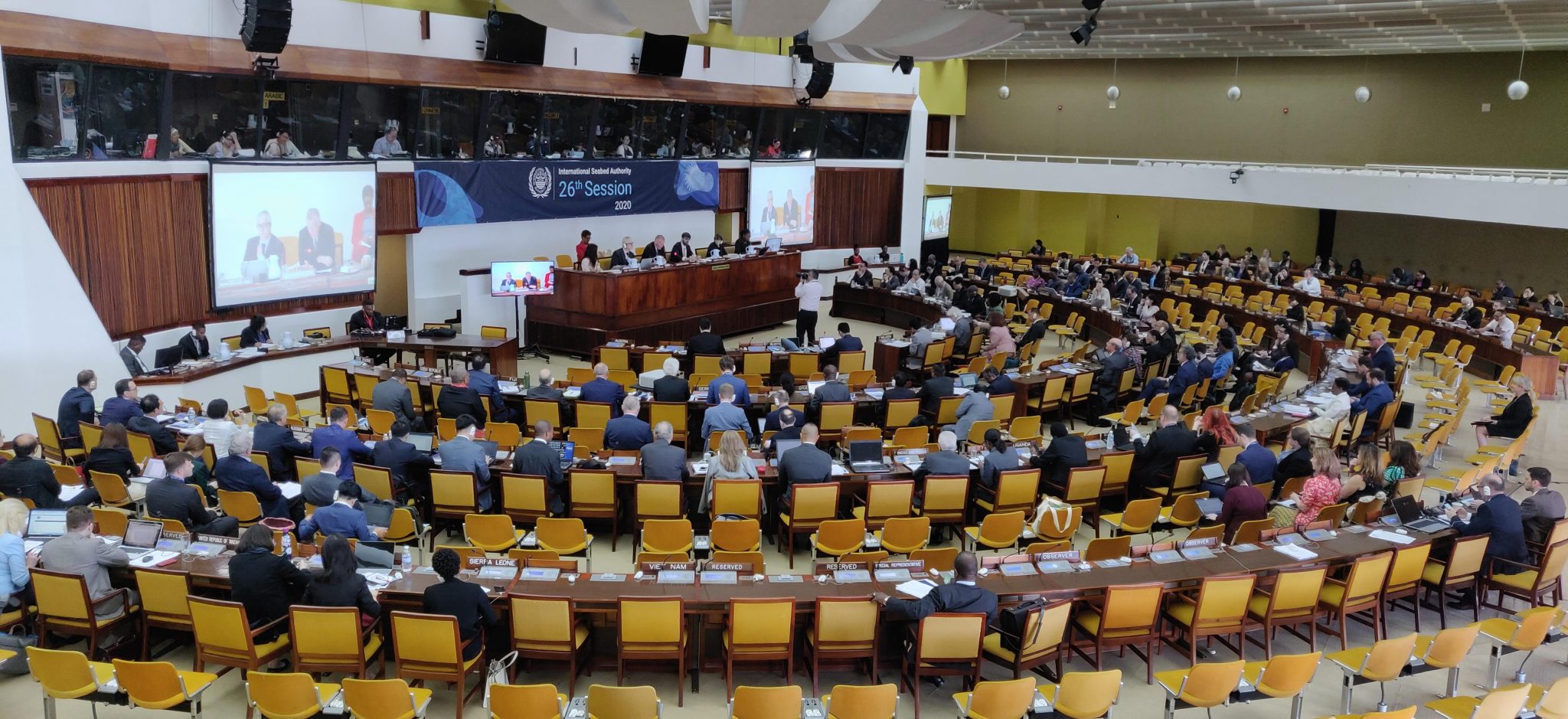
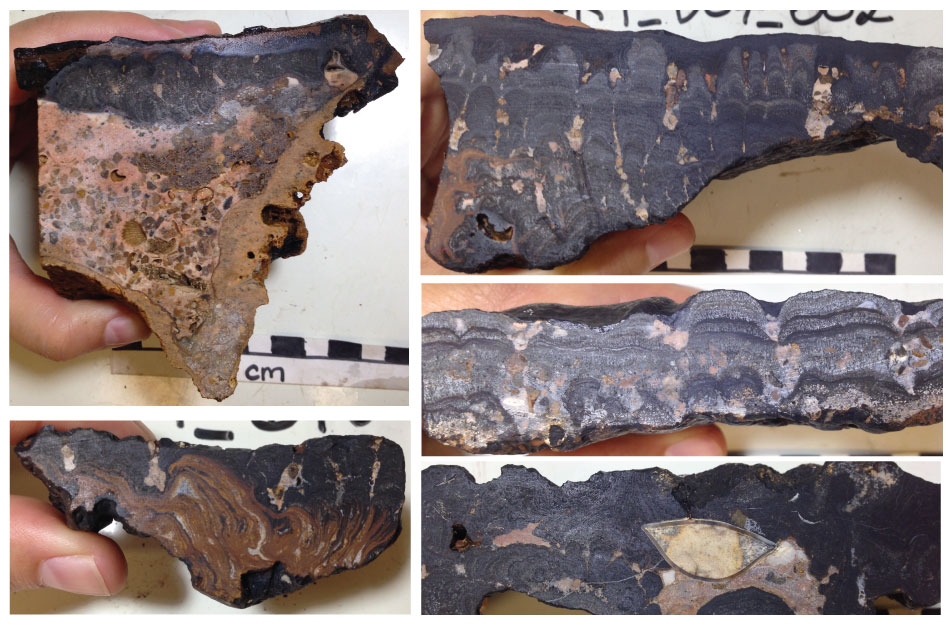
As in-person negotiations on the future of exploitation in the deep ocean resume this week in Kingston Jamaica, we reflect back on the last two years of development as reported on our sister site, the Deep-sea Mining Observer. This article first appeared on August 26, 2021.
The Republic of Nauru turned the deep-sea mining world on its head this summer when it invoked Article 15, colloquially known as the Trigger, starting a 2-year countdown on the finalization of mining regulations for polymetallic nodules in areas beyond national jurisdiction. This countdown means that commercial deep-sea mining could potentially commence within 3 years. But that commencement depends on a suite of benchmarks, both procedural and technological, that have yet to be met.
While Nauru and its deep-sea mining contractor, Nauru Ocean Resources Inc. (a wholly owned subsidiary of The Metals Company), emphasize the urgency of unlocking seafloor metals to accelerate the transition to a fossil fuel-free future, many stakeholders have expressed surprise at what they feel is a premature invocation of a rule designed to prevent oppositional member states from stonewalling progress on a mining code.
The two year clock doesn’t guarantee that a mining code will be complete within that time frame, but rather that either the mining code be finalized or a submitted Plan of Work be considered by the Council based on current and best-available standards and guidelines. Though The Metals Company has stated in the past that it would not support invoking Article 15 unless it was certain it had the backing of the majority of the Council, those political winds could easily change in the next three years, and the Council retains the authority to reject a Plan of Work.
It remains to be seen whether and if a mining code drafted under ticking clock of the two-year countdown will be more or less amenable to the preferences of deep-sea mining contractors and their sponsor states, but initial responses from delegations representing ISA Council members, the Legal and Technical Commission, and observers suggest that invoking Article 15 is just as likely to backfire on the Republic of Nauru and The Metals Company.
Read More “Two Years of Deep-sea Mining in Review: Has pulling the Trigger already backfired?” »