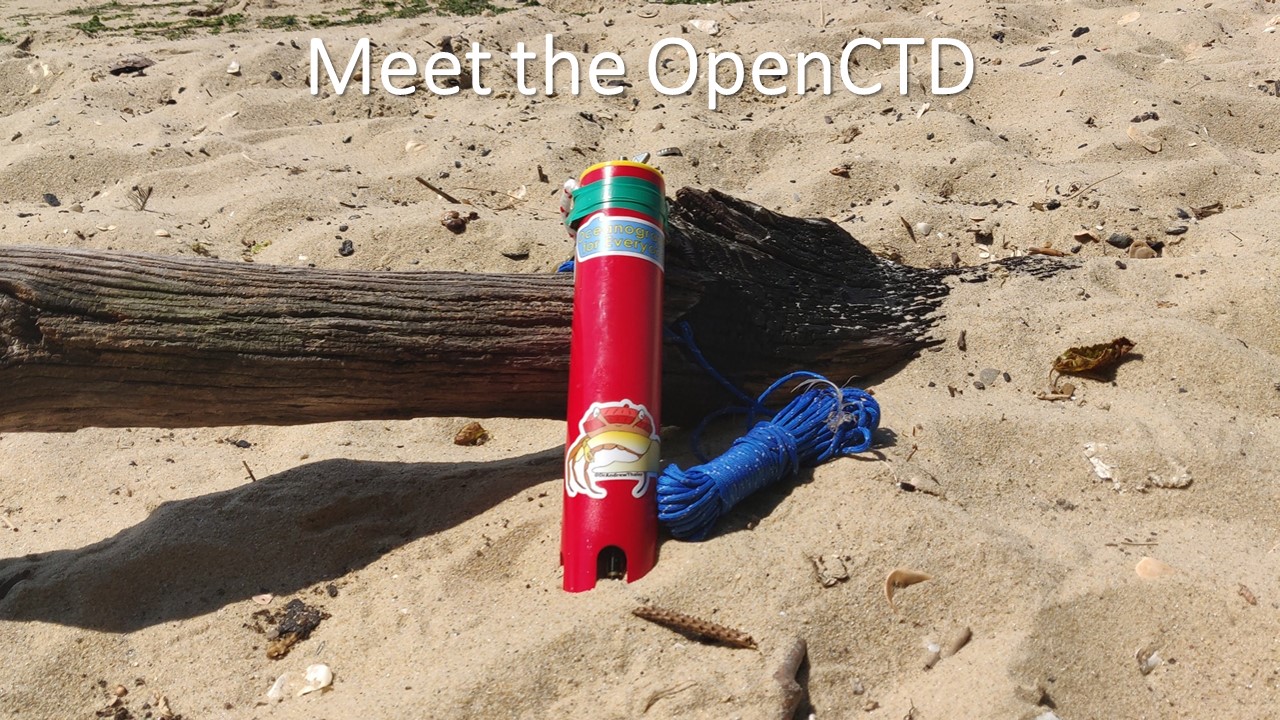
In 2013, Kersey Sturdivant and I embarked upon a quixotic quest to create an open-source CTD — the core tool of all oceanographic research that measures the baseline parameters of salinity, temperature, and depth. We weren’t engineers; neither of us had any formal training in electronics or sensing. And, full confession, we weren’t (and still aren’t) even oceanographers! What we were were post-doc marine ecologists working with tight budgets who saw a desperate need among our peers and colleagues for low-cost alternatives to insurmountably expensive equipment. And we had ties to the growing Maker and DIY electronics movements: Kersey through his work developing Wormcam and me through my involvement with OpenROV.
We had no idea what we were getting ourselves into.

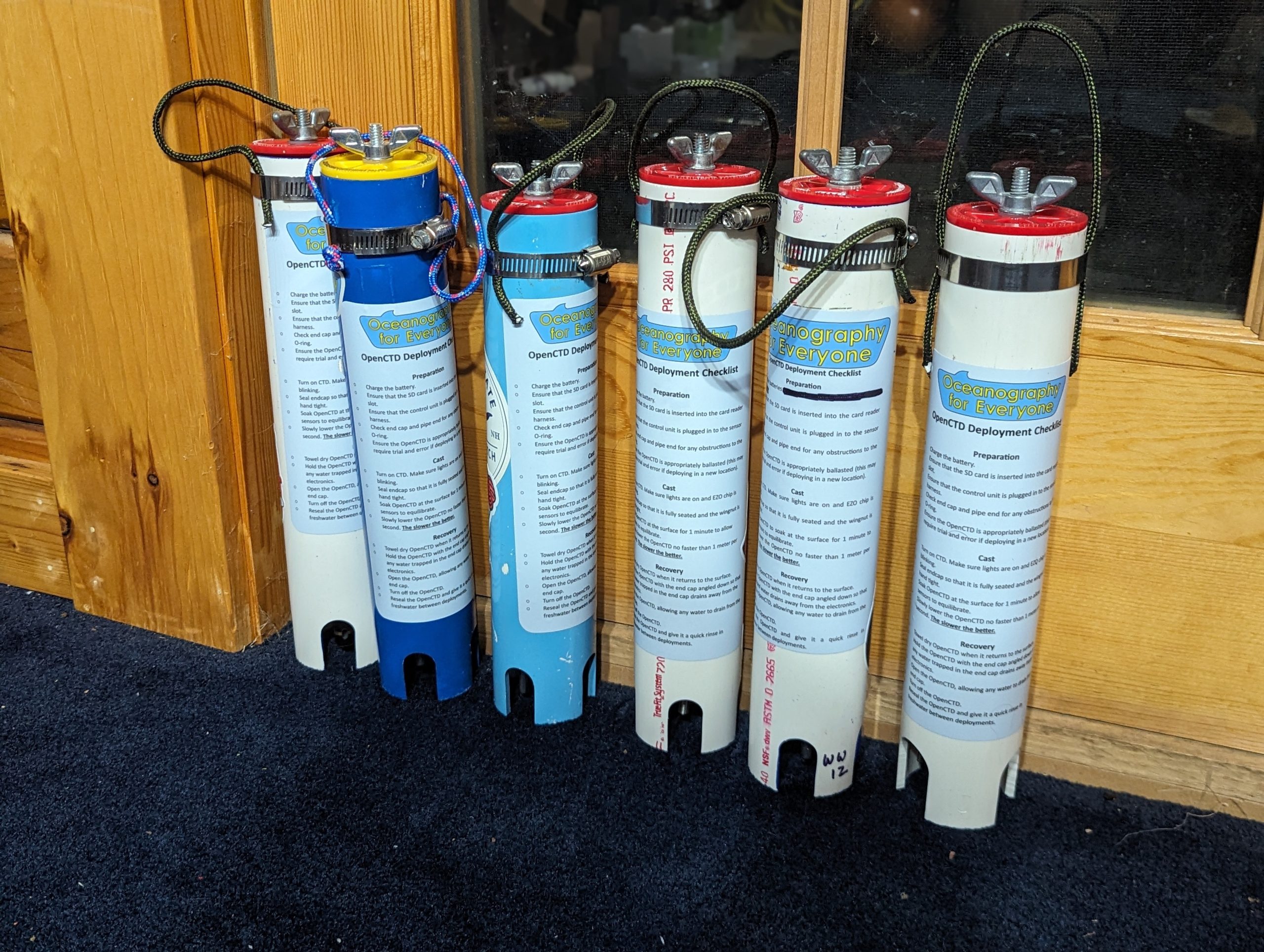
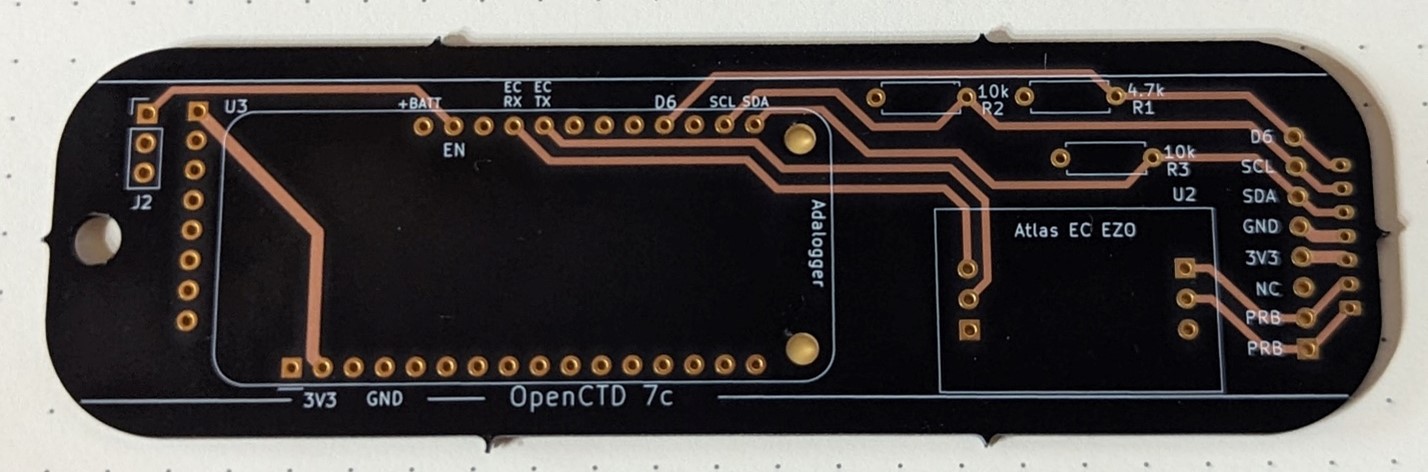
Seven years and five iterations later, we are releasing the long anticipated OpenCTD rev 2 as well as the comprehensive Construction and Operation Manual! OpenCTD rev 2 builds on over half a decade of iteration and testing, consultation with oceanographers, engineers, developers, and makers around the world, extensive coastal and sea trials, and a series of workshops designed to test and validate the assembly process.